💡 Your spinal disc doesn’t just “recover” with hydration while you sleep. It responds to what you do before you rest.
🟠 Your Discs Aren’t Lazy — They’re Just Dehydrated
Most people think spinal health and disc hydration is a waiting game: take the pressure off, rest a bit, and hope the body “fixes itself.” But that mindset overlooks one of the most basic truths of physiology: structure needs input.
Your intervertebral discs — the soft cushions between each vertebra — don’t have a direct blood supply. They rely entirely on your movement, posture, and hydration mechanics to stay supple and healthy. If you’ve ever felt stiff or achy in the morning despite a “good night’s sleep,” there’s a reason for that.
🧠 The Science of Disc Hydration — in Plain Speak
Discs rehydrate in two ways:
1. Passive Rehydration (Osmotic Pressure)
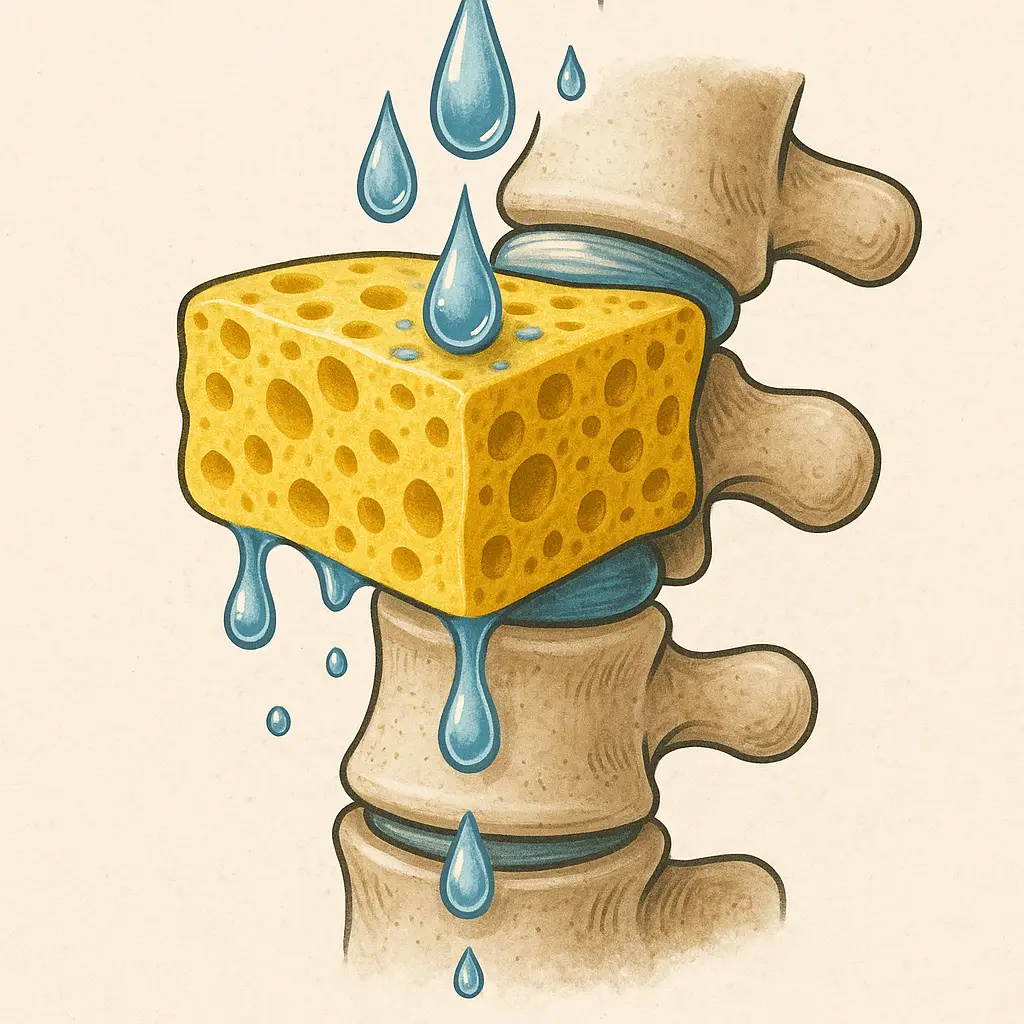
When you lie down at night, gravity is removed. This creates an osmotic gradient — water is slowly drawn back into the discs. Think of it like setting a sponge in a shallow bowl of water. It’ll eventually soak in… but only as much as its tissue allows.
2. Active Rehydration (Mechanical Stimulus)
When you de-coapt your spine through targeted movement — like ELDOA stretches — you create negative pressure and fascial tension. This primes the disc to pull in more fluid. It’s like squeezing and releasing that sponge right before soaking it — it absorbs far more water when prepped this way.
🌙 Why ELDOA “TV Stretching” Works So Well for Disc Hydration
“TV Stretching” is the term we use for doing your ELDOA decompression work 1–2 hours before bed. This timing allows you to:
- Decompress your spine actively
- Prime your discs to absorb water
- Then follow it with passive overnight rehydration
You’re combining two mechanisms, not relying on just one.
This is especially effective if you’re dealing with:
- Degenerative disc issues
- Postural compression from sitting or lifting
- Chronic stiffness that doesn’t resolve with sleep alone
🛠 Try This Tonight: 2-Step Reset (L5/S1 Focus)
Before bed, try this:
- Get into the L5/S1 ELDOA position, but keep your knees bent.
This protects the popliteal artery, which runs behind the knee and can be compressed during long-duration stretches with extended legs. - Stay in the posture passively — just hold the position and breathe for 5, 10, or even 15 minutes.
You’re not actively reaching or tensioning yet — just letting the spine settle and decompress through position alone. - Then do a single, focused ELDOA hold — no more than 1 minute.
Engage the full fascial lines. Create vertical tension. Be precise.
(Too long and you’ll reverse the effect — ELDOAs are about quality, not duration.) - Lie down and rest.
This primes your spine for both active and passive hydration during the night.
Try this for a few nights and feel the difference. It’s a strategy rooted in somatic intelligence — not guesswork.
🌀 Recovery Starts with Awareness
This is about more than hydration — it’s about being in your body enough to know what it needs and when.
If you’re curious how body awareness and healing are deeply connected, this Psychology Today overview of somatic therapy breaks it down beautifully. It echoes what we practice here — movement that starts with presence, not just position.
✅ Feel Different in the Morning — Not Just Rested
If you want to feel strong, tall, and fluid in the morning, you don’t need more sleep.
You need smarter pre-sleep recovery.
This approach is simple, targeted, and doesn’t take long. But it’s rooted in deep science and even deeper respect for the body’s rhythms.
🔗 Want help applying this to your specific structure?
Book a free 30–45 minute strategy call and we’ll walk through the right ELDOA and hydration approach for your spine.
Or join us for our monthly Free Community ELDOA class, to try it for yourself.
Follow the Thread—Where Movement, Fascia, and Freedom Align
Find more insight, reflection, and fascia-informed care across the platforms where we stay connected:









